Main Content
Rosmarinic acid: biosynthesis, regulation and evolution
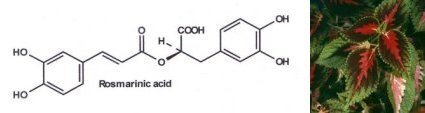
Rosmarinic acid is a common constituent of members of the families Lamiaceae and Boraginaceae, but is also found in other species, e.g. the hornwort Anthoceros and the fern Blechnum. Most probably this ester of caffeic acid and 3.4-dihydroxyphenyllactic acid serves as a constitutively accumulated preformed defense compound for the plant against pathogens and herbivores. Our interest is the elucidation of the enzymology and the regulation on enzyme and gene level of rosmarinic acid formation. This will show us when and where in the plant rosmarinic acid biosynthesis and accumulation is induced. Moreover, the evolutionary relationship of rosmarinic acid biosynthesis in lower and higher plants as well as the development of enzymes of rosmarinic acid biosynthesis from enzymes in primary metabolism are interesting topics. For this purpose, genes involved in rosmarinic acid biosynthesis are cloned from different plants and enzymes are crystallized and their structure elucidated.