Main Content
Quantum Cluster Equilibrium
The quantum cluster equilibrium (QCE) model of liquids and liquid mixtures describes a set of static clusters in chemical equilibrium. The chemical potential of each cluster is computed from standard thermochemical calculations using electronic structure theory and the rigid-rotor—harmonic-oscillator (RRHO) approximation. Van-der-Waals-type interactions are added to describe interactions between clusters. The partition function of this model system is an attempt to describe the partition function of the real system.

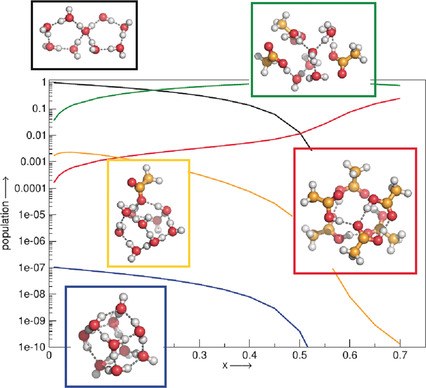
QCE gives the pressure- and temperature-dependent partition function of a liquid at moderate computational cost. It also provides access to the cluster populations, which can be used, among others, to predict equilibrium constants, such as the ionic product of water or acidity constants.
Images
1) Perlt, E.; von Domaros, M.; Kirchner, B.; Ludwig, R.; Weinhold, F. Predicting the Ionic Product of Water. Scientific Reports [Online] 2017, 7 (1). DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-10156-w. (accessed Sep 19, 2024)
2) Blasius, J.; Ingenmey, J.; Perlt, E.; von Domaros, M.; Hollóczki, O.; Kirchner, B. Predicting Mole‐fraction‐dependent Dissociation for Weak Acids. Angewandte Chemie International Edition [Online] 2019, 58 (10), 3212–3216. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201811839. (accessed Sep 19, 2024)