Main Content
Anaerobic toluene metabolism
The initial step of anaerobic toluene degradation is a stereospecific addition of the methyl group of toluene to the double bond of a fumarate cosubstrate, catalyzed by the glycyl-radical enzyme (R)-benzylsuccinate synthase. We are currently working on the reaction mechanism of this enzyme and its activation to the glycyl radical state. In addition, we are involved in developing its biotechnological applicability and in altering its substrate range and enantiospecificity. In addition, we are working on the structure-function relations of the other 5 enzymes of the pathway, which are involved in a b-oxidation pathway of benzylsuccinate to benzoyl-CoA and succinyl-CoA.
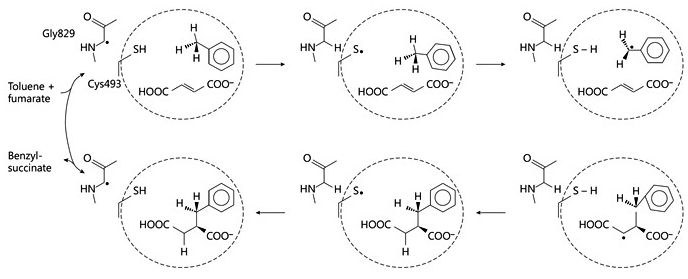
Fig. 1: Proposed reaction mechanism of benzylsuccinate synthase. © Seyhan D., Friedrich P., Szaleniec M., Hilberg M., Golding B. T., Buckel W. & Heider J. (2016) Elucidating the Stereochemistry of Enzymatic Benzylsuccinate Synthesis with Chirally Labeled Toluene. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 55, 11664-11667
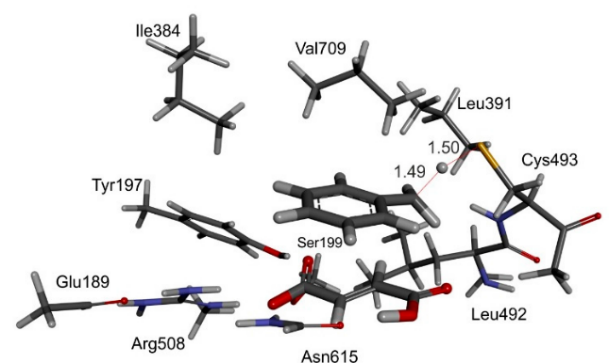
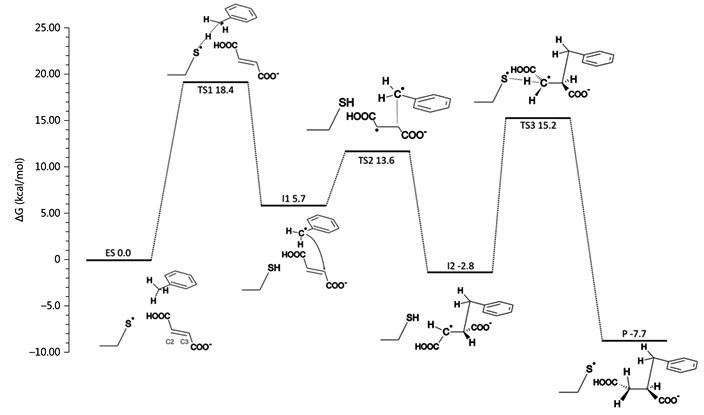
Fig. 2: left: computer model of bound toluene and fumarate in the active site of BSS, together with important amino acid residues; right: calculated energies of the proposed reaction path of BSS by quantum mechanics (QM) modelling. © Szaleniec M. & Heider J. (2016) Modeling of the reaction mechanism of enzymatic radical C-C coupling by benzylsuccinate synthase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17,514