Main Content
Identification and characterisation of the host interactome of LASV matrix protein Z
The LASV matrix protein Z has important structural and functional roles in the virus life cycle, such as regulation of viral RNA synthesis, orchestration of viral assembly and budding, and inhibition of the interferon-mediated immune response. In an effort to identify novel virus-host protein interactions of the LASV Z protein, we used proximity-dependent biotinylation (BioID2) as a mean of affinity purification coupled with mass spectrometry analysis to screen for physiologically relevant protein-protein interactions within living cells. Functional validation of selected interaction candidates is currently in progress to define the mechanistic and molecular details how these factors act in the viral life cycle. A better understanding of the molecular roles of host proteins during LASV infection will provide valuable insights into virus-host interactions and molecular pathogenesis of LASV, and provide a foundation for the rational design of new treatment strategies.
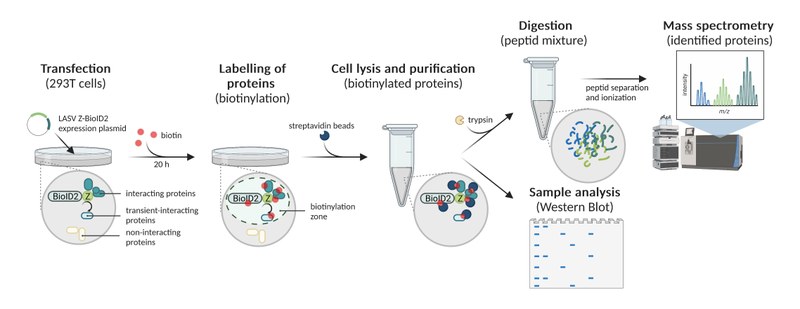
Identification of the cellular interactome of LASV matrix protein Z using BioID2 and mass spectrometry.