Main Content
Scientific projects research group Eva Herker
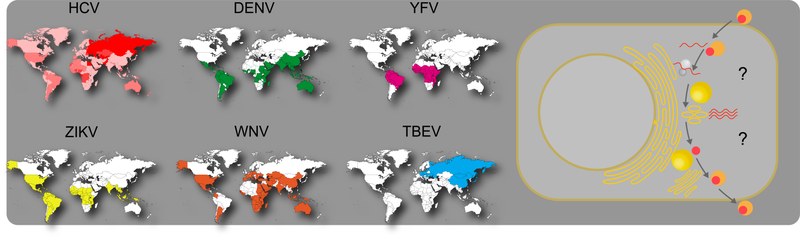
Global distribution of flaviviruses und scheme of the replication cycle.
Metabolic remodeling of the host cell is essential for successful viral replication. For example, positive-sense RNA viruses induce membrane rearrangements in the cytoplasm as replication centers. These vesicular structures are thought to both protect the viral RNA from recognition by the hostÕs antiviral defense and to concentrate factors and/or metabolites required for RNA replication. The membrane rearrangements differ between viruses and it is not yet clear which lipid metabolic pathways are hijacked for their formation. LDs, known as the major storage organelles for neutral lipids in cells, are also hubs of metabolic processes. Pathogens, including viruses like HCV and DENV, exploit unique aspects of LD biology to support their own replication and persistence within the host.
The goal of our research is to understand the interplay between viruses and their host to identify novel strategies for therapeutic intervention.