Main Content
TP5: Desmoglein-dependent signaling complexes in pemphigus

Summary
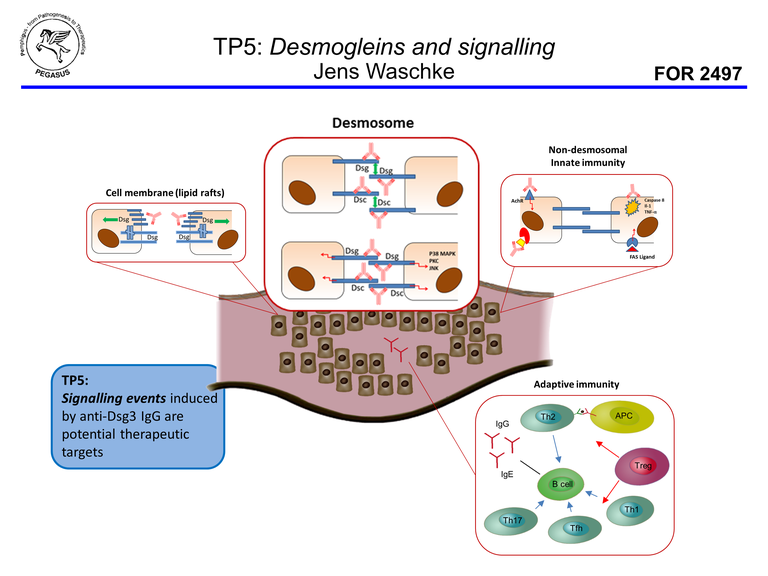
Binding of Dsg-specific IgG auto-ab to their desmosomal targets on epidermal keratinocytes leads to the induction of distinct signaling events. During the first funding period of PEGASUS we found that signaling pathways correlate with autoantibody profiles against Dsg1 and Dsg3 and proposed that pattern of signaling pathways may determine the clinical phenotype in pemphigus patients. Therefore, in the second funding period, we aim to clarify the role of Dsg1- and Dsg3-mediated signaling pathways for blister formation and will characterize the underlying mechanisms.
For Dsg1-mediated signaling we identified Ca2+ as activator for PKC and also ERK and for Dsg3-induced pathways Src and EGFR as important for loss of keratinocyte adhesion. In contrast, p38MAPK appears to be activated by autoantibodies against both Dsg1 and Dsg3. Similar as for p38MAPK before, we will characterize for signaling complexes coordinated by Dsg1 and Dsg3 how they regulate cytoskeletal anchorage and turnover of desmosomes. In order to do so, we will apply electron microscopy and STED imaging in human ex vivo models for skin and mucosa, which in part have been established recently. Because we identified increased cAMP as endogenous protective mechanism to rescue cell adhesion, we will investigate the underlying mechanisms and the therapeutic potential of the PDE4 inhibitor Apremilast.
These findings will be critical for our understanding of molecular mechanisms in pemphigus pathogenesis and may help to establish new therapeutic approaches to treat pemphigus patients.
Contact
Prof. Dr. Jens Waschke
Project leader TP5, Co-Speaker Pegasus
Department of Anatomy
Ludwig Maximilians University Munich
Pettenkoferstr. 11
D-80336 Munich
Tel +49 89 2180 72610
Fax +49 89 2180 72602
Email: jens.waschke@med.uni-muenchen.de
Team

From left to right:
Prof. Dr. Jens Waschke,
Michelle Hermann,
Silke Gotshy,
Dr. Thomas Schmitt,
Dr. Desalegn Egu





